Phylogenetic tree of infectious bronchitis virus

Dr. Milad Ibrahim Urabi
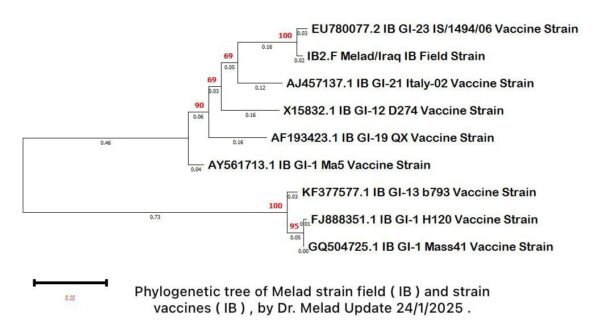
In this article, we talk about the phylogenetic tree of a field strain of infectious bronchitis virus (IB) and some of its associated vaccines.
Genetic clustering:
The field strain and treatment by Dr. Milad Ibrahim Arabi (IB2.F Melad/Iraq IB Field Strain) appear genetically close to vaccine strains such as GI-23 IS/1494/06 Vaccine Strain.
The field strain is genetically closer to the strains in the upper branch of the tree (GI-23, GI-21, and GI-12) than to strains such as H120 and Mass41 in the lower part.
Genetic distances:
The numbers on the lines (branches) represent genetic differences. Where I notice that there is a significant genetic difference between the strains in the upper and lower branch. The field strain shows a smaller genetic distance with the GI-23 vaccine compared to the other strains.
Bootstrap Values:
The values placed on the branches (e.g. 100, 95, 90) indicate the degree of reliability of the branch division. High values (e.g. 100) indicate strong support for the evolutionary relationships between the strains.
This tree can be used to determine how well vaccines are dealing with the field strain. Based on the tree, strains that are genetically close to the field strain (e.g. GI-23) may be more effective. Strains that are distant (e.g. Mass41 and H120) may be less effective, which necessitates updating vaccination programs.
Notes:
Based on the plot of this tree, the field strain may need specialized vaccines or modified vaccination programs to enhance its effectiveness. It also requires additional genetic analysis that may reveal more details about the relationship of the field strains to other vaccines.



